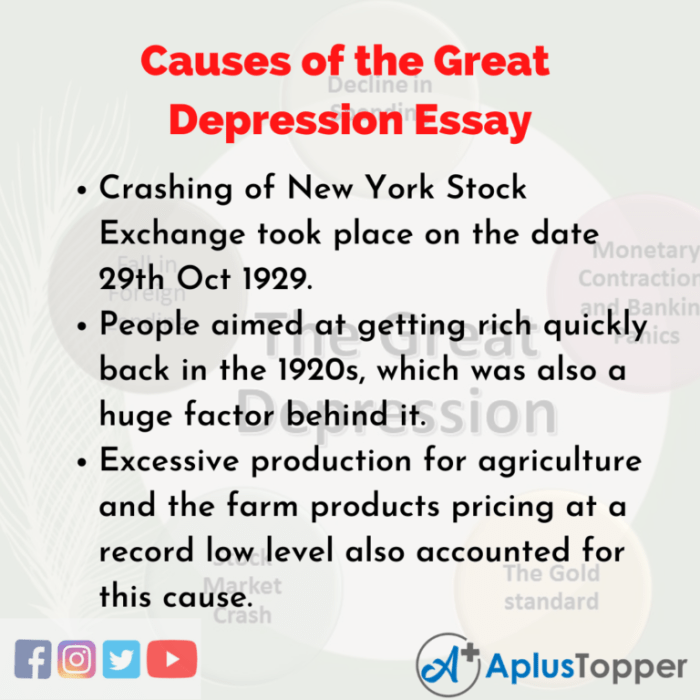
Essay about the great depression – The Great Depression, a cataclysmic economic downturn that ravaged the world in the 1930s, serves as a poignant reminder of the fragility of global economies and the profound impact they can have on societies.
Its far-reaching consequences extended beyond the realm of finance, leaving an indelible mark on the social, political, and cultural fabric of nations.
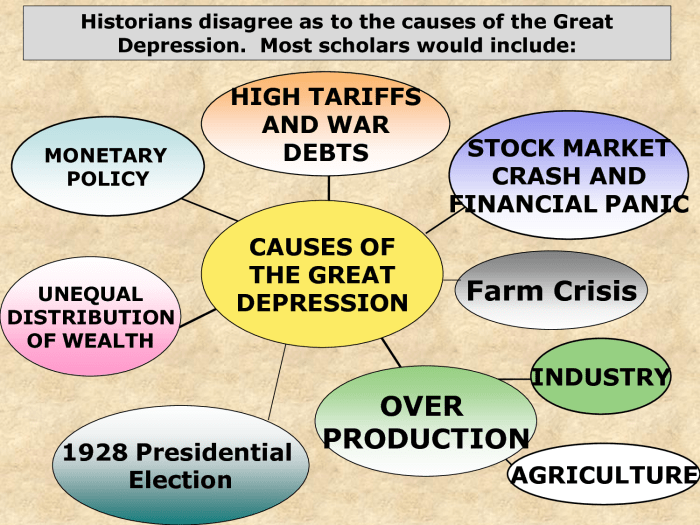
Economic Causes of the Great Depression
The Great Depression, the most severe economic downturn in modern history, was a complex event with multiple contributing factors. Economic causes played a significant role in triggering and exacerbating the crisis.
Overproduction and Underconsumption
Overproduction, a situation where supply exceeds demand, was a major contributor to the Great Depression. Industries had expanded rapidly during the 1920s, leading to a glut of goods. At the same time, wages had not kept pace with productivity, resulting in underconsumption.
Consumers lacked the purchasing power to absorb the surplus production.
Stock Market Crash of 1929
The stock market crash of 1929 was a pivotal event in the Great Depression. The collapse of stock prices wiped out billions of dollars in wealth and triggered a loss of confidence in the economy. This led to a sharp decline in investment and consumer spending, further deepening the economic crisis.
Industries Hard Hit
Several industries were particularly hard hit by the Great Depression. These included:
- Agriculture:Overproduction and falling prices devastated farmers.
- Manufacturing:Factories closed as demand for goods plummeted.
- Construction:Building projects were halted due to lack of investment.
- Retail:Sales plummeted as consumers cut back on spending.
Social Impact of the Great Depression: Essay About The Great Depression
The Great Depression brought widespread unemployment and poverty, leaving millions of Americans without jobs, homes, or basic necessities. It had a devastating impact on families and communities, causing widespread hardship and social unrest.
Unemployment and Poverty
The unemployment rate soared to an unprecedented 25% at the height of the Depression, leaving millions of Americans out of work. Many lost their homes and savings, and families struggled to put food on the table. Poverty became widespread, with an estimated 40% of Americans living below the poverty line.
Effects on Families and Communities
The Depression put a strain on families, as fathers lost their jobs and mothers struggled to make ends meet. Divorce rates rose, and many families were forced to rely on government assistance or charity. Communities were also affected, as businesses closed and tax revenues declined.
Schools and hospitals faced budget cuts, and social services were stretched to their limits.
Coping with Hardship
People coped with the economic hardship in various ways. Some turned to government assistance programs, such as the Works Progress Administration (WPA), which provided jobs for the unemployed. Others relied on the support of family and friends, or bartered goods and services to get by.
Many Americans also turned to religion for comfort and guidance during this difficult time.
Political Response to the Great Depression
The Great Depression sparked contrasting political responses, as exemplified by the policies of Herbert Hoover and Franklin D. Roosevelt.
Hoover’s Policies
Hoover’s approach emphasized laissez-faire economics and limited government intervention. Key policies included:
- Smoot-Hawley Tariff (1930):Raised tariffs to protect American industries, exacerbating global trade tensions.
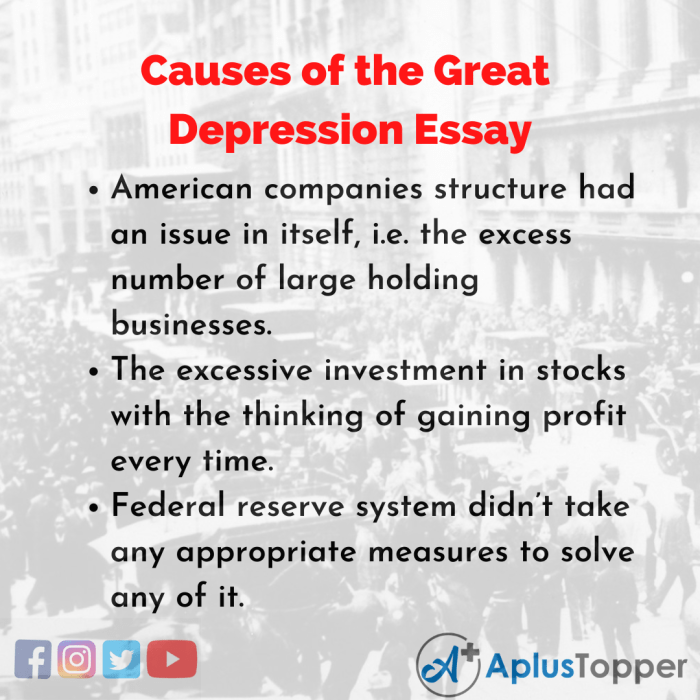
- Reconstruction Finance Corporation (1932):Provided loans to banks and businesses, but had limited impact due to strict eligibility criteria.
Roosevelt’s New Deal
Roosevelt’s New Deal represented a significant departure from Hoover’s approach. It aimed to stimulate the economy, provide relief to the unemployed, and reform the financial system.
- National Recovery Administration (NRA):Set codes of fair competition for industries, aimed at stabilizing prices and wages.
- Public Works Administration (PWA):Funded large-scale infrastructure projects to create jobs.
- Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC):Employed young men in conservation and environmental projects.
- Social Security Act (1935):Established a national system of unemployment insurance and old-age pensions.
The New Deal’s effectiveness remains debated. While it provided some relief and created jobs, it failed to fully restore economic prosperity. Critics argue that it prolonged the Depression by creating dependency on government programs.
International Impact of the Great Depression

The Great Depression did not confine its devastation to the United States; it spread like a contagion across the globe, leaving no continent untouched. The interconnectedness of the world economy ensured that the economic crisis in one country would have ripple effects far and wide.
Impact on Global Trade and Finance
The collapse of demand in the United States had a profound impact on global trade. As American imports plummeted, other countries saw their exports dwindle. This led to a sharp decline in global trade volumes, which in turn exacerbated the economic crisis.
The Great Depression also had a devastating impact on global finance. The collapse of the American stock market led to a loss of confidence in the international financial system. This made it difficult for countries to borrow money, which further slowed down economic growth.
Responses of Different Countries
Different countries responded to the Great Depression in different ways. Some countries, such as Germany and Japan, adopted aggressive expansionist policies that led to increased government spending and deficit financing. Other countries, such as France and the United Kingdom, pursued more conservative policies that focused on reducing government spending and balancing the budget.
There is no consensus on which approach was more effective in combating the Great Depression. However, it is clear that the Great Depression had a profound impact on the global economy and that its effects were felt far beyond the borders of the United States.
Cultural Impact of the Great Depression
The Great Depression profoundly influenced the cultural landscape of the 1930s, leaving an enduring mark on art, literature, and music.
The economic crisis fostered a widespread sense of disillusionment and social unrest, which found expression in the rise of social realism in art and literature. This movement sought to depict the harsh realities of everyday life for the working class and the poor, highlighting the struggles and suffering endured during the Depression.
Literature
Authors such as John Steinbeck and Erskine Caldwell captured the experiences of migrant workers, sharecroppers, and the urban poor in their works. Steinbeck’s novel The Grapes of Wrath(1939) became a powerful indictment of the social injustices faced by migrant workers during the Dust Bowl, while Caldwell’s Tobacco Road(1932) depicted the poverty and desperation of sharecroppers in the rural South.
Art
In art, the Great Depression influenced the development of the American Scene movement, which focused on depicting everyday American life and often reflected the hardships faced by ordinary people. Artists such as Grant Wood and Thomas Hart Benton created works that celebrated rural and small-town America, while others, like Ben Shahn, used their art to raise awareness of social and economic issues.
Music
The Great Depression also had a significant impact on music, particularly in the realm of folk and blues. The economic hardship and social unrest of the era gave rise to a surge in protest songs, which expressed the frustrations and aspirations of the working class.
Folk singers such as Woody Guthrie and Lead Belly became symbols of the Depression era, their songs chronicling the struggles of the common people.
Lessons Learned from the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a devastating worldwide financial meltdown that began in the United States in the 1930s. The catastrophe had far-reaching effects, both domestically and internationally, and provided important lessons for preventing or mitigating the impacts of future economic crises.
Economic and Social Factors Contributing to the Great Depression
- Overproduction and Speculation:The Roaring Twenties saw a surge in production and speculative investments, leading to an unsustainable economic bubble.
- Weak Banking System:Inadequate regulation and risky lending practices contributed to bank failures and a loss of public confidence in the financial system.
- International Factors:Global economic imbalances, such as high tariffs and war debts, hindered international trade and exacerbated the depression.
Importance of Government Intervention during Economic Downturns
The Great Depression highlighted the critical role of government intervention in stabilizing the economy during downturns. Governments implemented various measures, including:
- Fiscal Stimulus:Governments increased spending and reduced taxes to boost demand and create jobs.
- Monetary Policy:Central banks lowered interest rates and expanded the money supply to encourage borrowing and investment.
- Financial Regulation:Governments enacted regulations to strengthen the banking system and prevent future crises.
Recommendations for Preventing or Mitigating Future Economic Crises, Essay about the great depression
Based on the lessons learned from the Great Depression, several recommendations have been proposed to prevent or mitigate the effects of future economic crises:
- Stronger Financial Regulation:Governments should implement robust regulations to prevent excessive risk-taking and ensure the stability of the financial system.
- Diversified Economy:Countries should diversify their economies to reduce dependence on specific industries or sectors.
- International Cooperation:Global economic imbalances should be addressed through international cooperation and coordination.
- Fiscal and Monetary Policy Preparedness:Governments and central banks should be prepared to implement fiscal and monetary stimulus measures in the event of an economic downturn.
Popular Questions
What were the primary causes of the Great Depression?
Overproduction, underconsumption, and the stock market crash of 1929 were key contributing factors.
How did the Great Depression impact society?
Widespread unemployment, poverty, and social unrest plagued communities during this period.
What were the key policies implemented in response to the Great Depression?
Herbert Hoover’s policies focused on limited government intervention, while Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal programs aimed to stimulate economic recovery.