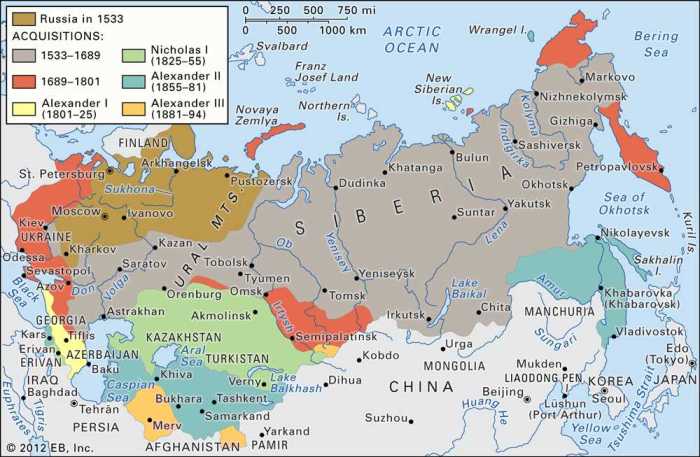
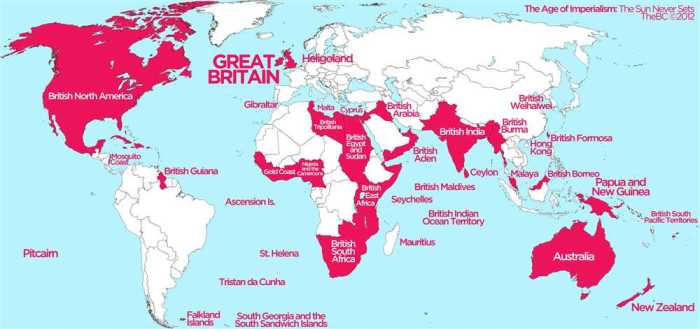
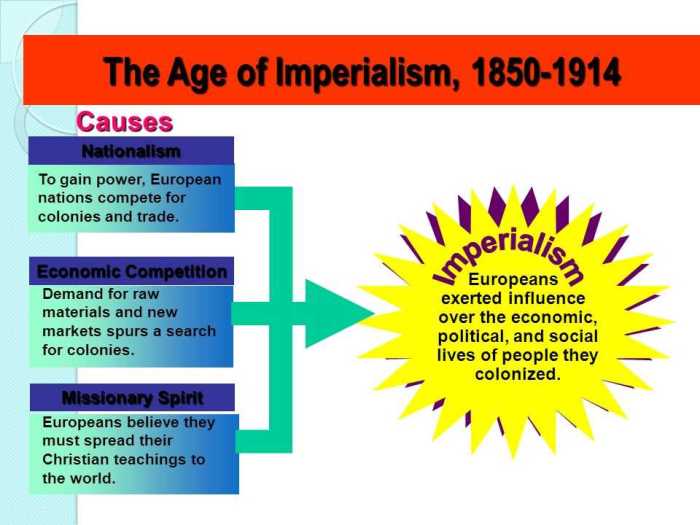
Annotated Map of Imperialism Answer Key unveils the intricate tapestry of global power dynamics and their profound impact on societies and cultures. This comprehensive resource offers a captivating journey through the historical context, geographical implications, and lasting legacy of imperialism, providing a multifaceted understanding of this transformative era.
By examining annotated maps, we delve into the strategies and motivations of major European powers, unraveling the complex relationships between colonizers and colonized regions. These maps illuminate the economic, social, and cultural consequences of imperialism, shaping our understanding of the interconnectedness of nations and the enduring effects of historical events.
Historical Context of Imperialism: Annotated Map Of Imperialism Answer Key
Imperialism, the extension of a nation’s power and influence over other regions, has a long and complex history. Its origins can be traced back to the European Renaissance and the Age of Exploration, when European powers began to seek new sources of wealth and trade.
The Industrial Revolution further fueled imperialism, as European nations competed for access to raw materials and markets.The major European powers involved in imperialism included Britain, France, Spain, Portugal, and Germany. Each nation had its own unique strategies and motivations for acquiring colonies.
For example, Britain focused on establishing a vast empire through trade and conquest, while France pursued a policy of assimilation, seeking to integrate its colonies into the French nation.
Key Imperial Territories, Annotated map of imperialism answer key
Imperial powers established colonies in various parts of the world, including Africa, Asia, and the Americas. These territories were often chosen for their strategic location, natural resources, or economic potential. Some of the most significant imperial territories included:
- India: A vast and populous region, India was a major prize for European powers. Britain established control over India through the East India Company, which gradually expanded its influence until it controlled most of the subcontinent.
- China: China was another major target of imperialism. European powers sought to establish trading posts and concessions in China, leading to the Opium Wars and the eventual partition of the country into spheres of influence.
- Congo: The Congo was a major source of rubber and other raw materials. King Leopold II of Belgium established a brutal regime in the Congo, which led to widespread human rights abuses.
Quick FAQs
What is the purpose of an annotated map of imperialism?
Annotated maps of imperialism provide a visual representation of the historical expansion and control of territories by European powers. They offer detailed information about key imperial territories, their significance, and the impact of imperialism on regions and cultures.
How do annotated maps help us understand imperialism?
Annotated maps provide a comprehensive overview of the geographical extent of empires, allowing us to trace the expansion and decline of imperial powers. They also highlight the economic, social, and cultural consequences of imperialism, facilitating a deeper understanding of its global impact.
What are some common features included on annotated maps of imperialism?
Annotated maps of imperialism typically include information such as territorial boundaries, dates of acquisition, key events, economic resources, cultural influences, and the impact of imperialism on indigenous populations.