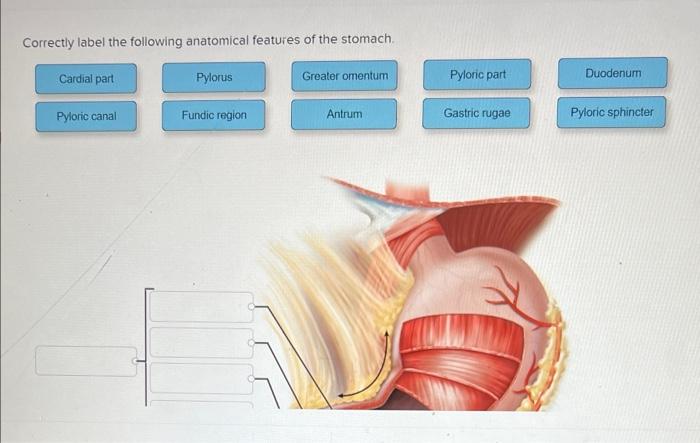
Correctly label the following anatomical features of the stomach – Correctly labeling the anatomical features of the stomach is crucial for accurate medical diagnosis, treatment planning, and surgical procedures. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the stomach’s anatomy, explains the importance of precise labeling, and discusses common errors to avoid.
The stomach, a vital organ in the digestive system, plays a significant role in food digestion and nutrient absorption. Understanding its intricate anatomical features is essential for healthcare professionals to effectively manage gastrointestinal disorders and ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Anatomical Features of the Stomach
The stomach is a J-shaped organ located in the upper left quadrant of the abdominal cavity. It is responsible for receiving, storing, and partially digesting food before passing it on to the small intestine. The stomach has several distinct anatomical features, each of which plays a specific role in the digestive process.
Regions of the Stomach, Correctly label the following anatomical features of the stomach
The stomach is divided into four main regions:
- Cardia:The cardia is the point where the esophagus joins the stomach. It contains a muscular sphincter that prevents food from regurgitating back into the esophagus.
- Fundus:The fundus is the dome-shaped region located above the cardia. It stores food and secretes gastric juices.
- Body:The body is the main central portion of the stomach. It secretes gastric juices and mixes food with them.
- Antrum:The antrum is the funnel-shaped region located at the distal end of the stomach. It mixes food with gastric juices and propels it into the small intestine.
Layers of the Stomach Wall
The stomach wall is composed of four layers:
- Mucosa:The mucosa is the innermost layer of the stomach wall. It contains glands that secrete gastric juices, as well as a layer of mucus that protects the stomach lining from the acidic environment.
- Submucosa:The submucosa is a layer of connective tissue that lies beneath the mucosa. It contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels.
- Muscularis externa:The muscularis externa is a layer of smooth muscle that lies beneath the submucosa. It is responsible for mixing food with gastric juices and propelling it through the stomach.
- Serosa:The serosa is the outermost layer of the stomach wall. It is a thin layer of connective tissue that covers the stomach and attaches it to surrounding structures.
Other Anatomical Features
In addition to the regions and layers of the stomach wall, there are several other anatomical features that are important for the digestive process:
- Gastric glands:The gastric glands are located in the mucosa of the stomach. They secrete gastric juices, which contain hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and other enzymes that help to break down food.
- Pyloric sphincter:The pyloric sphincter is a muscular valve located at the junction of the stomach and the small intestine. It controls the flow of food from the stomach into the small intestine.
- Greater curvature:The greater curvature is the convex side of the stomach. It is located along the left side of the stomach.
- Lesser curvature:The lesser curvature is the concave side of the stomach. It is located along the right side of the stomach.
Detailed FAQs: Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of The Stomach
What are the most common errors in labeling the anatomical features of the stomach?
Common errors include confusing the fundus with the body, mistaking the pyloric antrum for the pyloric canal, and misidentifying the greater curvature as the lesser curvature.
Why is it important to correctly label the anatomical features of the stomach?
Precise labeling facilitates accurate communication among healthcare professionals, ensures proper diagnosis and treatment planning, and minimizes errors during surgical procedures.