Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive production possibilities curve frontier worksheet answers, meticulously crafted to illuminate the intricacies of this fundamental economic concept. This guide delves into the theoretical underpinnings, graphical representations, and practical applications of the PPC, empowering you with a profound understanding of its significance in economic decision-making.
Unravel the mysteries of the PPC’s shape, explore the factors that influence its shifts, and uncover the underlying assumptions that govern its behavior. Our interactive HTML table brings the PPC to life, allowing you to visualize the trade-offs inherent in producing goods and services.
Delve into the concepts of efficiency and inefficiency, identifying points on the PPC that represent optimal resource allocation and potential areas for improvement.
Understanding the Production Possibilities Curve
The production possibilities curve (PPC) is a graphical representation of the maximum possible combinations of two goods or services that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology.
The PPC is typically drawn as a concave curve, indicating that there is a trade-off between producing one good and the other. As more of one good is produced, less of the other can be produced.
The assumptions underlying the PPC include: full employment of resources, fixed technology, and no externalities.
Graphical Representation of the PPC
| Goods | Services |
|---|---|
| 0 | 100 |
| 25 | 75 |
| 50 | 50 |
| 75 | 25 |
| 100 | 0 |
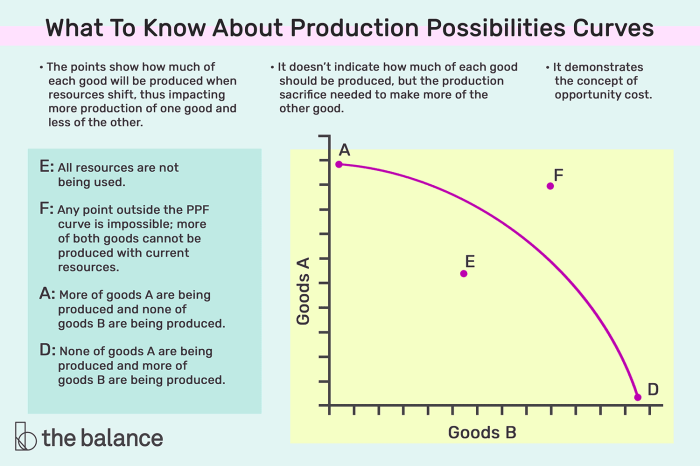
The PPC shows that there is a trade-off between producing goods and services. As more goods are produced, less services can be produced, and vice versa.
The axes of the graph are labeled “Goods” and “Services”, and the units of measurement are arbitrary.
Efficiency and Inefficiency on the PPC
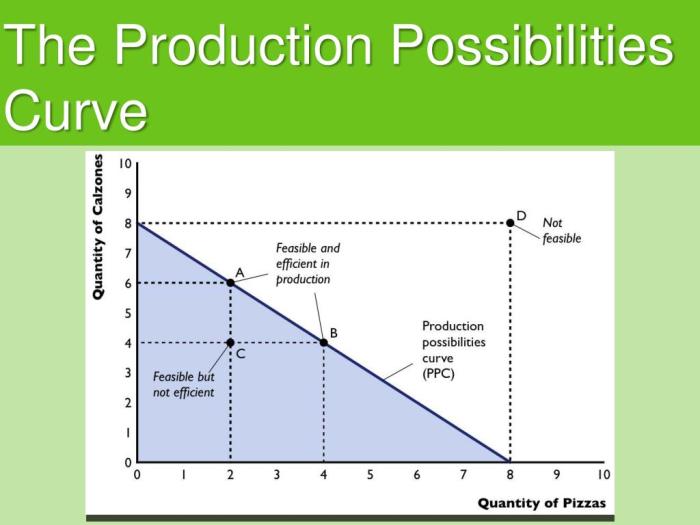
Productive efficiency occurs when an economy is producing on the PPC. Points on the PPC represent efficient production because the economy is using its resources to produce the maximum possible output of both goods.
Points inside the PPC represent inefficient production because the economy is not using its resources efficiently. Points outside the PPC represent unattainable production because the economy does not have the resources or technology to produce that combination of goods.
Shifts in the PPC
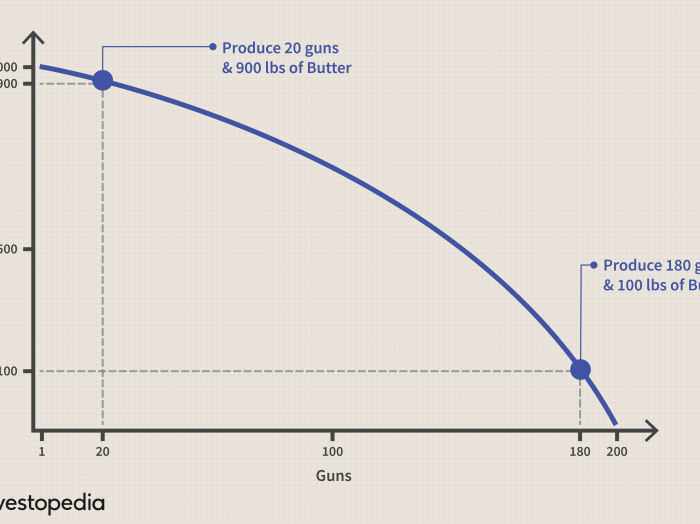
The PPC can shift outward or inward due to changes in technology, resource availability, or consumer preferences.
- Technological advancementscan shift the PPC outward by allowing the economy to produce more of both goods with the same resources.
- Increased resource availabilitycan also shift the PPC outward by providing the economy with more resources to use in production.
- Changes in consumer preferencescan shift the PPC inward or outward depending on the demand for the two goods.
Applications of the PPC: Production Possibilities Curve Frontier Worksheet Answers

The PPC can be used to analyze economic policy decisions. For example, the PPC can be used to show the trade-offs involved in pursuing different policy objectives, such as economic growth and environmental protection.
The PPC has also been used to inform policy-making in the real world. For example, the PPC was used to analyze the economic impact of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of the production possibilities curve?
The production possibilities curve (PPC) is a graphical representation of the maximum combinations of two goods or services that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology. It illustrates the trade-offs involved in producing one good over another, highlighting the opportunity cost of each decision.
How can the PPC be used to analyze economic growth?
The PPC can be used to assess the potential for economic growth by examining shifts in the curve. Outward shifts indicate an increase in productive capacity, while inward shifts suggest a decline. Factors such as technological advancements, resource availability, and changes in consumer preferences can influence the position of the PPC.
What are the assumptions underlying the PPC?
The PPC assumes that the economy operates at full employment, resources are fully utilized, and technology remains constant. These assumptions simplify the analysis and allow for a clear understanding of the trade-offs involved in production.