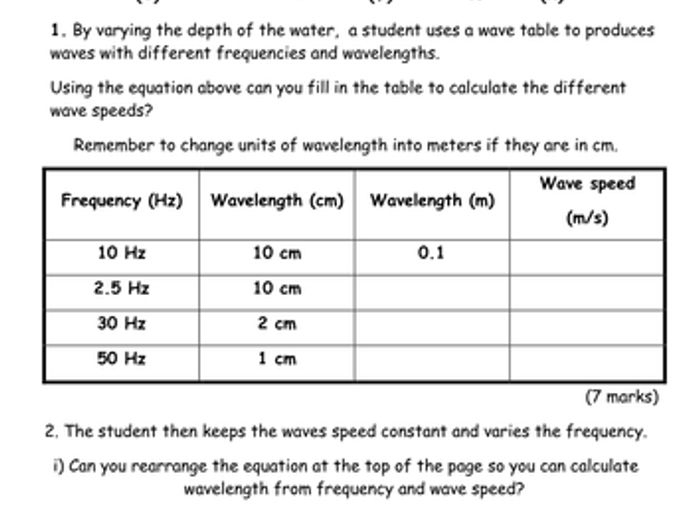
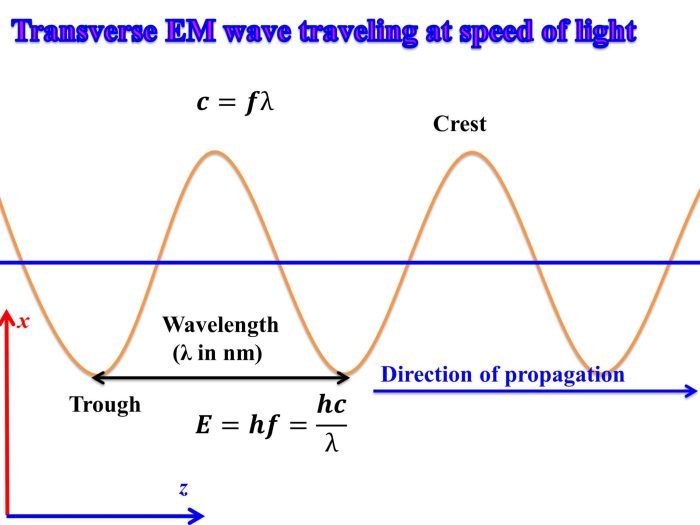
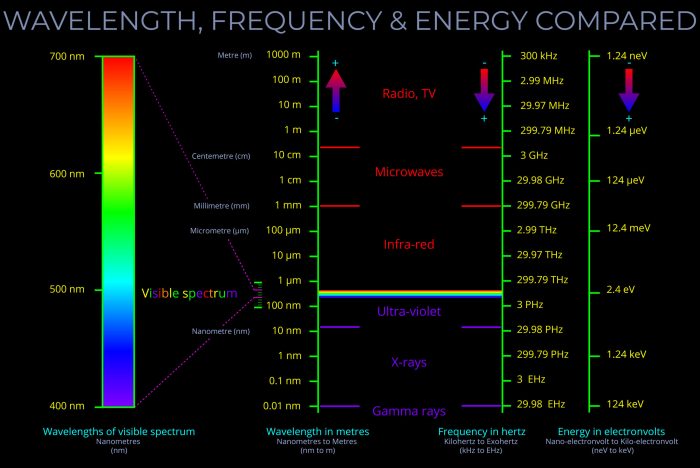
The Frequency Wavelength and Energy Worksheet is a comprehensive resource designed to enhance understanding of the fundamental concepts of frequency, wavelength, and energy in the context of the electromagnetic spectrum. This worksheet provides a structured approach to learning and applying these principles through a series of engaging exercises and problems.
This worksheet explores the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy, providing an equation that quantifies this relationship. It also delves into the methods used to measure these quantities and discusses the limitations of these measurement techniques.
Frequency, Wavelength, and Energy
In the realm of electromagnetic radiation, frequency, wavelength, and energy are intertwined concepts that govern the behavior and characteristics of electromagnetic waves. Understanding the relationship between these quantities is crucial for comprehending the nature of electromagnetic radiation and its diverse applications.
Frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), represents the number of oscillations or cycles completed by an electromagnetic wave per second. Wavelength, denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ), is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of the wave. Energy, symbolized by E, is the amount of energy carried by a single photon, the fundamental unit of electromagnetic radiation.
The relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy is mathematically expressed by the equation:
E = hf = hc/λ
where h is Planck’s constant (6.63 × 10 -34J s).
This equation reveals that energy is directly proportional to frequency and inversely proportional to wavelength. Higher frequency waves have shorter wavelengths and higher energy, while lower frequency waves have longer wavelengths and lower energy.
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a vast range of frequencies, wavelengths, and energies, spanning from low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays. Different regions of the spectrum correspond to different types of electromagnetic radiation, such as visible light, microwaves, and X-rays.
Measuring Frequency, Wavelength, and Energy
Measuring frequency, wavelength, and energy of electromagnetic radiation is essential for characterizing and identifying different types of radiation.
Frequency can be measured using a variety of techniques, including frequency counters, spectrum analyzers, and resonant circuits. Wavelength can be determined using interferometers, diffraction gratings, or rulers.
Energy measurement is typically performed using detectors that convert the energy of photons into electrical signals. These detectors include photodiodes, photomultipliers, and calorimeters.
The accuracy and precision of these measurement techniques are crucial for accurate characterization of electromagnetic radiation. However, limitations exist, such as the sensitivity of detectors and the resolution of measuring instruments.
Applications of Frequency, Wavelength, and Energy, Frequency wavelength and energy worksheet
The concepts of frequency, wavelength, and energy find widespread applications across various fields:
- Communication:Different frequency ranges are utilized for radio, television, and mobile phone communication.
- Medicine:X-rays and gamma rays are used for medical imaging and radiation therapy.
- Remote Sensing:Microwaves and infrared radiation are employed in satellite imagery and remote sensing applications.
The choice of frequency range for a particular application depends on factors such as penetration depth, resolution, and bandwidth requirements.
Worksheet Activities
Exercise 1:Calculate the frequency of a radio wave with a wavelength of 100 m.
Exercise 2:Determine the wavelength of an X-ray with an energy of 100 keV.
Exercise 3:Plot the electromagnetic spectrum and identify the different regions corresponding to various types of radiation.
Exercise 4:Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using microwaves for communication compared to radio waves.
Popular Questions: Frequency Wavelength And Energy Worksheet
What is the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy?
Frequency, wavelength, and energy are inversely related. As frequency increases, wavelength decreases, and energy increases. This relationship is expressed by the equation E = hf, where E is energy, h is Planck’s constant, and f is frequency.
How are frequency, wavelength, and energy used in communication?
Frequency, wavelength, and energy are used in communication to transmit information over various distances. Different frequency ranges are allocated for different types of communication, such as radio, television, and mobile phones.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using different frequency ranges for communication?
Different frequency ranges have different advantages and disadvantages for communication. Lower frequencies have longer wavelengths and can travel longer distances, but they have lower bandwidth and are more susceptible to interference. Higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths and higher bandwidth, but they have a shorter range and are more easily absorbed by obstacles.